Back to Climate Atlas
1.0 Data
1.1 Data Sources
1.2 Station Selection Criteria
1.2.1 Station Selection Criteria for Snow Elements
1.2.2 Station Selection Criteria for non-Snow Elements
2.0 Element Descriptions

1.0 Data

1.1 Data Sources
Several data sources were used for generating the atlas maps including Daily Cooperative Summary of the Day (NOAA, 1995), Climatic Data Normals (NOAA, 1994), Snow Climatology (NOAA, 1997), Hourly First-Order Observations (NOAA, 1999), Daily Summaries of Hourly First-Order Observations (NOAA, 1999), Monthly Normals for Atypical Elements (NOAA, 1997), and the Monthly Normals of Temperature, Precipitation, and Degree Days for the U.S. (Clim81) (NOAA, 1994).

1.2 Station Selection Criteria
The number of stations used for generating the various grids was dependent on the data source: 3779 stations from the snow climatology data set, 6662 precipitation stations from the Clim81 set, 4775 temperature stations from Clim81, 8198 temperature stations from the cooperative observer data set, and 230 stations from the first-order data set.

1.2.1 Station Selection Criteria for Snow Elements
The snow elements were obtained from the snow climatology (NOAA, 1997). The criteria for handling missing data for computing the mean monthly and annual normal snowfall differed for the coop stations and the first order (WBAN) stations. For the coop stations, the total snowfall had no tolerance for missing data. If even one day was missing in a month, the total snowfall was not be computed for that year's month. Consequently, the number of years with non-missing data varied with month. For first order stations, the criteria were not as stringent as for coop stations. The WMO guidelines for computing normals were used. They defined a missing month as having (1) five or more consecutive daily values missing, or (2) a total of eleven or more missing daily values in the month.
The median daily value for a month had no tolerance for missing data. All days in a month had to have data in order for a median daily value to be computed for that year-month. The number of days with snowfall or snow depth parameters had no tolerance for missing data. Data for leap days were included in the analysis. Due to this fact and due to rounding error, the sum of the values for the = 0 or >= 0.1 inch (1.0 inch for snow depth) thresholds may not exactly equal the number of days in the month.
The daily extreme and date of occurrence parameters had a greater tolerance for missing data. Data were analyzed even if a month had up to 5 days missing. This could result in apparent discrepancies between these and other parameters.
In the "number of days with" computations, if a month had fewer than 6 missing days, then the "number of days" tallies were pro-rated by a factor of (pos/obs), where pos = the number of days in the month and obs = the number of non-missing days in the month. Leap days were included in the analysis, but the results were pro-rated as above to conform to a 28-day February. The pro-rating feature and possible rounding errors may result in the following apparent inconsistencies: (1) the sum of the monthly values may not equal the sum of the annual value, and (2) the cross-element sums (e.g., number of days with snowfall [or snow depth] = 0. plus the number of days>= 0.1 inch for snowfall [1.0 inch for snow depth]) may not equal the maximum possible monthly or annual value. In all cases the apparent inconsistencies are minor.

1.2.2 Station Selection Criteria for non-Snow Elements
Generally, no more than 5 missing days in a month of daily values were allowed for that data-month to be valid and no more than 15 missing data-months during the 1961-1990 period for an element-month to be valid. An additional requirement for hourly data sets was that at least three observations were required in the morning hours and three in the evening hours so that a bias was not introduced.

2.0 Element Descriptions
General:
Unless otherwise noted, all values were based on normals for the period 1961-1990.
Monthly normals were computed for as many stations as practical. In order to be included, the station had to have at least 10 years of monthly temperature data and 10 years of monthly precipitation data from the period 1961-90. Computation of annual values were made from 12 monthly values, provided that no months were missing.

Index of Element References (Map Names)
(Click on an Element Description Below for a Shortcut to its Explanation)

Each element in the Climate Atlas was constructed from databases at the National Climatic Data Center or other governmental entities as appropriate. The descriptions in this section document the source of the station data subsequently used in producing the Climate Atlas maps. The description begins by documenting the source data set, original units, and element units. Then, the method of computation and other pertinent information is provided.
Unless otherwise noted, all elements were computed for the 30-year period 1961-1990. Monthly values were computed for as many stations as practical. In order to be included, the station had to have at least 10 years of monthly temperature data and 10 years of monthly precipitation data from the period 1961-1990. Computation of annual values were made from the 12 monthly values, provided that no months were missing.

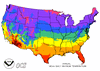
A. Temperature
A.1
Mean Daily Maximum Temperature:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's U.S. National 1961-1990 Climate Normals (NOAA, 1994b). The original data is in whole degrees Fahrenheit. This element is computed to tenths of a degree Fahrenheit.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the monthly means. The monthly means were computed from the daily values. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean values.
A.2
Mean Extreme Maximum Temperature:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Cooperative Summary of the Day (TD-3200) database (NCDC, 1995). The original data is in whole degrees Fahrenheit. This element is computed to tenths of a degree Fahrenheit.
The monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the highest daily maximum temperatures for a given month. The annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the highest daily temperatures for each calendar year. Daily maximum temperatures were the highest observed temperatures for the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station.
A.3
Record Extreme Maximum Temperature:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Cooperative Summary of the Day (TD-3200) database (NCDC, 1995). The original data is in whole degrees Fahrenheit. This element is computed to tenths of a degree Fahrenheit.
The monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year highest daily maximum temperature for a given month. The annual value was computed by taking the highest daily maximum temperature for the full 30-year period. Daily maximum temperatures were the highest observed temperatures for the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station.
A.4
Mean Daily Minimum Temperature:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's U.S. National 1961-1990 Climate Normals (NOAA, 1994b). The original data is in whole degrees Fahrenheit. This element is computed to tenths of a degree Fahrenheit.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the monthly means. The monthly means were computed from the daily values. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean values.
A.5
Mean Extreme Minimum Temperature:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Cooperative Summary of the Day (TD-3200) database (NCDC, 1995). The original data is in whole degrees Fahrenheit. This element is computed to tenths of a degree Fahrenheit.
The monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the lowest daily minimum temperatures for a given month. The annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the lowest daily temperature for each calendar year. Daily minimum temperatures were the lowest observed temperatures for the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station.
A.6
Record Extreme Minimum Temperature:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Cooperative Summary of the Day (TD-3200) database (NCDC, 1995). The original data is in whole degrees Fahrenheit. This element is computed to tenths of a degree Fahrenheit.
The monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year lowest daily minimum temperature for a given month. The annual value was computed by taking the lowest daily maximum temperature for the full 30-year period. Daily minimum temperatures were the lowest observed temperatures for the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station.
A.7
Mean Daily Average Temperature:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's U.S. National 1961-1990 Climate Normals (NOAA, 1994b). The original data is in whole degrees Fahrenheit. This element is computed to tenths of a degree Fahrenheit.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the monthly means. The monthly means were computed from the daily values. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean values.
A.8
Mean Daily Temperature Range:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's U.S. National 1961-1990 Climate Normals (NOAA, 1994b). The original data is in whole degrees Fahrenheit. This element is computed to tenths of a degree Fahrenheit.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the monthly means. The monthly means were computed from the daily values. The monthly daily temperature range value was computed from the mean of the sum of the differences between daily maximum and daily minimum temperature. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean values.
A.9
Last 32 Degree Fahrenheit Temperature in Spring:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Cooperative Summary of the Day (TD-3200) database (NCDC, 1995). The original data is in whole degrees Fahrenheit. This element is given as a date range.
The date of occurrence of the last 32 degree Fahrenheit temperature observation in spring was based on the median, mean, and extreme dates of such occurrence from 30 years of daily minimum temperature values, respectively. If at least one 32 degree Fahrenheit temperature was observed in the first six months of the calendar year, but a 32 degree Fahrenheit temperature did not occur in at least one-half of the years of available data, then the station was designated "RARE FREEZE." If no 32 degree Fahrenheit temperatures were observed in the first six months of the calendar year, then the station was designated "NO FREEZE." Daily minimum temperatures were the lowest observed temperatures for the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station.
A.10
First 32 Degree Fahrenheit Temperature in Autumn:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Cooperative Summary of the Day (TD-3200) database (NCDC, 1995). The original data is in whole degrees Fahrenheit. This element is given as a date range.
The date of occurrence of the first 32 degree Fahrenheit temperature observation in autumn was based on the median, mean, and extreme dates of such occurrence from 30 years of daily minimum temperature values, respectively. If at least one 32 degree Fahrenheit temperature was observed in the last six months of the calendar year, but a 32 degree Fahrenheit temperature did not occur in at least one-half of the years of available data, then the station was designated "RARE FREEZE." If no 32 degree Fahrenheit temperatures were observed in the last six months of the calendar year, then the station was designated "NO FREEZE." Daily minimum temperatures were the lowest observed temperatures for the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station.
A.11
Median/Mean Length of Freeze-Free Period:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Cooperative Summary of the Day (TD-3200) database (NCDC, 1995). The original data is in whole degrees Fahrenheit. This element is given as the number of whole days.
The length of the freeze-free period was based on the difference between the median and mean dates, respectively, of the last 32 degree Fahrenheit temperature in spring (Element TEMP09) and the first 32 degree Fahrenheit temperature in autumn (Element TEMP10). If either element was designated "RARE FREEZE" the station was excluded from the database. If both elements were designated "NO FREEZE," then this element was designated the same. If only one element was designated "NO FREEZE," then the station was excluded. Daily minimum temperatures were the lowest observed temperatures for 24 hours ending at the time of observation for a given station.
A.12
Mean Number of Days with Temperatures>= 90 Degrees Fahrenheit (70 F for AK):
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Cooperative Summary of the Day (TD-3200) database (NCDC, 1995). The original data is in whole degrees Fahrenheit. This element is given as the number of whole days.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the count of days where the maximum temperature was at or above 90 degrees Fahrenheit (70 F for AK) for a given month. Daily maximum temperatures were the highest observed temperatures for the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean values.
A.13
Mean Number of Days with Temperatures <= 32 Degrees Fahrenheit:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Cooperative Summary of the Day (TD-3200) database (NCDC, 1995). The original data is in whole degrees Fahrenheit. This element is given as the number of whole days.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the count of days where the minimum temperature was at or below 32 degrees Fahrenheit for a given month. Daily minimum temperatures were the lowest observed temperatures for the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean values.
A.14
Mean Total Heating Degree Days:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's U.S. National 1961-1990 Climate Normals (NOAA, 1994b). The original data is in whole degrees Fahrenheit. This element is given to whole degree days.
Heating degree day values were derived from a base of 65 degrees Fahrenheit. Simple arithmetic procedures were not applied to obtain the heating degree day values. Instead, the rational conversion formulae developed by Thom (1954, 1966) were used. These formulae allow the adjusted mean temperature normals and their standard deviations to be converted to degree day normals with uniform consistency. In some cases this procedure will yield a small number of degree days for months when degree days may not otherwise be expected. This results from statistical considerations of the formulae. The annual degree day normals were calculated by adding the corresponding monthly degree day normals.
A.15
Record Maximum Heating Degree Days:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Cooperative Summary of the Day (TD-3200) database (NCDC, 1995). The original data is in whole degrees Fahrenheit. This element is given to whole degree days.
Heating degree day values were derived from a base of 65 degrees Fahrenheit. Simple arithmetic procedures were applied to obtain the heating degree days for a given month - namely, the daily temperature averages were subtracted from 65, and then all days in a month were summed. The highest maximum monthly value of heating degree days for a given month was then selected. Similarly, the highest maximum monthly value of heating degree days for the full 30-year period was selected as the annual value.
A.16
Mean Total Cooling Degree Days:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's U.S. National 1961-1990 Climate Normals (NOAA, 1994b). The original data is in whole degrees Fahrenheit. This element is given to whole degree days.
Cooling degree day values were derived from a base of 65 degrees Fahrenheit. Simple arithmetic procedures were not applied to obtain the cooling degree day values. Instead, the rational conversion formulae developed by Thom (1954, 1966) were used. These formulae allow the adjusted mean temperature normals and their standard deviations to be converted to degree day normals with uniform consistency. In some cases this procedure will yield a small number of degree days for months when degree days may not otherwise be expected. This results from statistical considerations of the formulae. The annual degree day normals were calculated by adding the corresponding monthly degree day normals.
A.17
Record Maximum Cooling Degree Days:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Cooperative Summary of the Day (TD-3200) database (NCDC, 1995). The original data is in whole degrees Fahrenheit. This element is given to whole degree days.
Cooling degree day values were derived from a base of 65 degrees Fahrenheit. Simple arithmetic procedures were applied to obtain the cooling degree days for a given month - namely, the daily temperature averages were subtracted by 65, and then all days in a month were summed. The highest maximum monthly value of cooling degree days for a given month was then selected. Similarly, the highest maximum monthly value of cooling degree days for the full 30-year period was selected as the annual value.
A.18
Mean Dew Point Temperature:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Surface Airways Hourly (TD-3280) database (NOAA, 2000a). The original data is in whole degrees Fahrenheit. This element is computed to tenths of a degree Fahrenheit.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the monthly means. The monthly means were computed from the daily values. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean values.
A.19
Mean Maximum Dew Point Temperature:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Surface Airways Hourly (TD-3280) database (NOAA, 2000a). The original data is in whole degrees Fahrenheit. This element is computed to tenths of a degree Fahrenheit.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the maximum daily dew point temperatures for a given month. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly maximum daily dew point temperatures.
A.20
Mean Minimum Dew Point Temperature:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Surface Airways Hourly (TD-3280) database (NOAA, 2000a). The original data is in whole degrees Fahrenheit. This element is computed to tenths of a degree Fahrenheit.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the minimum daily dew point temperatures for a given month. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly minimum daily dew point temperatures. 
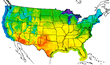
B. Precipitation
B.1
Mean Total Precipitation
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's U.S. National 1961-1990 Climate Normals (NOAA, 1994b). The original daily data and the element are in hundredths of an inch, with daily trace values designated as zero.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the monthly means. The monthly means were computed from the sum of the daily precipitation values for a given month. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean values.
B.2
Mean Maximum Daily Precipitation:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Cooperative Summary of the Day (TD-3200) database (NCDC, 1995). The original data and this element are measured in hundredths of an inch, with daily trace values designated as zero.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the maximum daily precipitation values for a given month. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean maximum daily precipitation values.
B.3
Record Total Precipitation:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Cooperative Summary of the Day (TD-3200) database (NCDC, 1995). The original data and this element are measured to one-hundredths of an inch, daily trace values designated as zero.
The monthly values were computed by taking the highest monthly precipitation total for a given month over the 30-year period. The annual value was computed by taking the highest annual total based on the sum of monthly totals for a calendar year over the 30-year period. Monthly totals were computed as the sum of measurable (non-zero, non-trace) daily precipitation values for all the days in a given month.
B.4
Mean Number of Days with Measurable Precipitation:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Cooperative Summary of the Day (TD-3200) database (NCDC, 1995). The original data and this element are given in hundredths of an inch. This element is given as number of whole days.
The monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the number of days with measurable precipitation (at least 0.01 inch) for a given month. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean number of days with measurable precipitation. 
C. Snow
C.1
Mean Total Snowfall:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's United States Snow Climatology (TD-9641M) database (NCDC, 1999c). The original data and this element are measured to a tenth of an inch, with daily trace values designated as zero.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the sum of daily snowfall values for a given month. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean values.
C.2
Mean Maximum Daily Snowfall:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's United States Snow Climatology (TD-9641M) database (NCDC, 1999c). The original data and this element are given in tenths of an inch, with daily trace values designated as zero.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the maximum daily snowfall values for a given month. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean maximum daily snowfall values.
C.3
Record Total Snowfall:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's United States Snow Climatology (TD-9641M) database (NCDC, 1999c). The original data and this element are given in tenths of an inch, with daily trace values designated as zero.
The monthly record total snowfall values were computed by taking the highest monthly snowfall total for a given month over the 30-year period. Monthly totals were computed as the sum of measurable (non-zero, non-trace) daily snowfall values for all the days in a given month. The annual value was computed by taking the highest annual total based on the sum of monthly totals for a calendar year over the 30-year period.
C.4
Mean Snow Depth:
This element was computed using snow depth data from the National Climatic Data Center's United States Snow Climatology (TD-9641M) database (NCDC, 1999c). The original snow depth data and this element are given in whole inches, with daily non-zero values of less than 0.5 inch designated a trace.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the sum of daily snow depth values for a given month. No annual value was computed. Daily snow depth measurements were based on the depth of snow on the ground at the time of observation for a given station. In computing the monthly means, daily trace values of snow depth were treated as a value of zero.
C.5
Mean Number of Days with Measurable Snowfall (Thresholds):
This element was computed using snowfall data from the National Climatic Data Center's United States Snow Climatology (TD-9641M) database (NCDC, 1999c). The original snowfall data is given to a tenth of an inch. This element is given as the number of whole days.
The 29-year mean of the number of days with snowfall at or above the four thresholds: 0.1 inch, 1.0 inch, 5.0, inches and 10.0 inches were computed for the snow season, August 1 - July 31. The first snow season commenced on August 1, 1961 and the last snow season ended on July 31, 1990.
C.6
Mean Number of Days with Measurable Snow Depth (Thresholds):
This element was computed using snow depth data from the National Climatic Data Center's United States Snow Climatology (TD-9641M) database (NCDC, 1999c). The original snow depth data is given to a whole inch. This element is given as the number of whole days.
The 29-year mean of the number of days with snow depth amounts at or above the three thresholds: 1 inch, 5 inches, and 10 inches were computed for the snow season, August 1 - July 31. The first snow season commenced on August 1, 1961 and the last snow season ended on July 31, 1990. Daily snow depth measurements were based on the depth of snow on the ground at the time of observation for a given station. In computing the monthly means, daily trace values of snow depth were treated as a value of zero.
C.7
Dates of First/Last Snowfall:
This element was computed using snowfall data from the National Climatic Data Center's United States Snow Climatology (TD-9641M) database (NCDC, 1999c). The original snowfall data is given to a tenth of an inch. This element is given as a date range.
The median and extreme dates of the first and last snowfall are presented within approximately biweekly ranges within the snowfall season (August - July). The median date is the 29-year median of the first or last date of measurable snowfall (at least 0.1 inch). Similarly, the extreme date is the absolute first or last date of measurable snowfall within the 29-year period. If no snow was observed for at least one-half of the years with available data, then the station was designated "RARE SNOW." If no snow was observed for any of the years with available data, then the station was designated "NO SNOW." The 29-year median and extreme dates were computed using snow season periods from August 1 - July 31. The first snow season commenced on August 1, 1961 and the last snow season ended on July 31, 1990. Daily snowfall measurements were based on the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station. In computing the monthly means, daily trace values of snowfall were treated as a value of zero.
C.8
Probability of Measurable Snowfall in a Snow Season:
This element was computed using snowfall data from the National Climatic Data Center's United States Snow Climatology (TD-9641M) database (NCDC, 1999c). The original snowfall data is given to a tenth of an inch. This element is given as a percentage.
The probability of measurable snow is the probability that a snowfall of at least 0.1 inch will be observed within a given snow season (August 1 - July 31). The probability is based on the 29 annual periods from August 1 - July 31, with the first period beginning August 1, 1961 and the last period ending July 31, 1990. Daily snowfall measurements were based on the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station. In computing the probabilities, daily trace values of snowfall were treated as a value of zero.
C.9
Probability of a White Christmas:
This element was computed using snow depth data from the National Climatic Data Center's United States Snow Climatology (TD-9641M) database (NCDC, 1999c). The original snow depth data is given to a tenth of an inch. This element is given as a percentage.
The probability of a white Christmas is the probability that a snow depth of at least 1 inch will be observed on December 25. The probability was computed using snow depth observations for December 25, for the full period of record for a given station, not just 1961-1990. Daily snowfall measurements were based on the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station. In computing the probabilities, daily trace values of snowfall were treated as zero. 
D. Wind
D.1
Mean Wind Speed
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Monthly Normals for Atypical Elements (TD-9641) database (NOAA, 1997b). The original data is given in knots. This element is given in miles per hour.
The monthly values of mean wind speed were computed by taking the 30-year mean of monthly wind speed for a given month. Monthly wind speeds were computed from the mean of daily wind speed observations. Daily wind speeds were computed as the mean of all 1-minute wind speed observations during the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station. The annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean values.
D.2
Mean Wind Speed and Prevailing Direction:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Monthly Normals for Atypical Elements (TD-9641) database (NOAA, 1997b). For wind speed, the original data is in knots and this element is in miles per hour. For prevailing wind direction, both the original data and this element are in coded directions, where 1=wind from the NNE and 16=wind from the N. Wind vectors are presented as arrows flying with the prevailing wind.
The monthly values of mean wind speed were computed by taking the 30-year mean of monthly wind speed for a given month. Monthly wind speeds were computed from the mean of daily wind speed observations. Daily wind speeds were computed as the mean of all 1-minute wind speed observations during the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean values.
The monthly values of prevailing wind direction were computed by taking the 30-year mean of prevailing wind directions for a given month. Monthly prevailing wind directions were computed as the most common daily prevailing wind direction. Daily wind directions were computed as the most common prevailing direction of all 1-minute wind direction observations during the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean values.
D.3
Fastest Mile of Wind
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Summary of the Day First Order (TD-3210) database (NOAA, 2000b). The original data and this element are given in whole miles per hour.
The monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the speed of daily observations with the fastest mile of wind. The annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean values. The fastest mile of wind was recorded by stations having triple or multiple register type recording instruments. The speed of a mile of wind occurring in the shortest time was used. This was determined by measuring the jogs on the chart made by the one mile contacts of the anemometer.
D.4
Mean Occurrences of Peak Gust>= 30 MPH:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Summary of the Day First Order (TD-3210) database (NOAA, 2000a). The original data is in knots and was reported as the 5-second peak gust for the day. This element is given in whole days.
For a given month, the mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the monthly count of days where the peak wind gust was at or above 30 miles per hour. Monthly counts of days with the identified peak gust were the sum of days where at least one peak gust observation exceeded the identified threshold. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly counts. The yearly counts were computed by summing their 12 monthly counts.
D.5
Mean Occurrences of Peak Gust>= 40 MPH:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Summary of the Day First Order (TD-3210) database (NOAA, 2000a). The original data is in knots and was reported as the 5-second peak gust for the day. This element is given in whole days.
For a given month, the mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the monthly count of days where the peak wind gust was at or above 40 miles per hour. Monthly counts of days with the identified peak gust were the sum of days where at least one peak gust observation exceeded the identified threshold. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly counts. The yearly counts were computed by summing their 12 monthly counts.
D.6
Mean Occurrences of Peak Gust>= 50 MPH:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Summary of the Day First Order (TD-3210) database (NOAA, 2000a). The original data is in knots and was reported as the 5-second peak gust for the day. This element is given in whole days.
For a given month, the mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the monthly count of days where the peak wind gust was at or above 50 miles per hour. Monthly counts of days with the identified peak gust were the sum of days where at least one peak gust observation exceeded the identified threshold. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly counts. The yearly counts were computed by summing their 12 monthly counts.
D.7
Mean Extreme 1% Wind Speed:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Surface Airways Hourly (TD-3280) database (NOAA, 2000a). The original data is given in knots. This element is given in miles per hour.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the mean extreme 1% wind speed for a given month. The annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the extreme 1% wind speed for each calendar year. Monthly and annual mean extreme wind speeds for the identified percentile were computed by determining the percentile from all hourly averaged wind speed observations for the month and year.
D.8
Mean Extreme 5% Wind Speed:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Surface Airways Hourly (TD-3280) database (NOAA, 2000a). The original data is given in knots. This element is given in miles per hour.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the mean extreme 5% wind speed for a given month. The annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the extreme 5% wind speed for each calendar year. Monthly and annual mean extreme wind speeds for the identified percentile were computed by determining the percentile from all hourly averaged wind speed observations for the month and year.
D.9
Mean Extreme 10% Wind Speed:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Surface Airways Hourly (TD-3280) database (NOAA, 2000a). The original data is given in knots. This element is given in miles per hour.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the mean extreme 10% wind speed for a given month. The annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the extreme 10% wind speed for each calendar year. Monthly and annual mean extreme wind speeds for the identified percentile were computed by determining the percentile from all hourly averaged wind speed observations for the month and year. 
E. Pressure
E.1
Mean Sea Level Pressure:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Surface Airways Hourly (TD-3280) database (NOAA, 2000a). The original data and this element are given to a tenth of a millibar.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the monthly means. The monthly means were computed from the daily values. The daily values were computed from the mean of observations for the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean values.
E.2
Mean Maximum Sea Level Pressure:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Surface Airways Hourly (TD-3280) database (NOAA, 2000a). The original data and this element are given to a tenth of a millibar.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of maximum sea level pressure for a given month. The monthly maximum value was the maximum of all daily values for a given month. The daily value was the maximum observation for the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly maximum values.
E.3
Mean Minimum Sea Level Pressure:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Surface Airways Hourly (TD-3280) database (NOAA, 2000a). The original data and this element are given to a tenth of a millibar.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of minimum sea level pressure for a given month. The monthly minimum value was the minimum of all daily values for a given month. The daily value was the minimum observation for the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly minimum values.
E.4
Record Maximum Sea Level Pressure:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Surface Airways Hourly (TD-3280) database (NOAA, 2000a). The original data and this element are given to a tenth of a millibar.
The monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year highest daily maximum sea level pressure for a given month. The annual value was computed by taking the highest daily maximum sea level pressure for the full 30-year period. Daily maximum pressures were the highest observed pressures for the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station.
E.5
Record Minimum Sea Level Pressure:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Surface Airways Hourly (TD-3280) database (NOAA, 2000a). The original data and this element are given to a tenth of a millibar.
The monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year lowest daily minimum sea level pressure for a given month. The annual value was computed by taking the lowest daily minimum sea level pressure for the full 30-year period. Daily minimum pressures were the lowest observed pressures for the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station. 
F. Days With
F.1
Mean Number of Days with Temperatures>= 90 Degrees F (70 F for AK)oF
(Please See Item A.12)
F.2
Mean Number of Days with Temperatures <= 32oF
(Please See Item A.11)
F.3
Mean Number of Days with Measurable Precipitation
(Please See Item B.4))
F.4
Mean Number of Days with Freezing Precipitation:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Monthly Normals for Atypical Elements (TD-9641) database (NOAA, 1997b). The original precipitation data is given to a hundredth of an inch. This element is given as the number of whole days.
The monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the number of days with at least one occurrence of freezing rain or freezing drizzle for a given month. The daily values included observations for the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean number of days with freezing rain or freezing drizzle.
F.5
Mean Number of Days with Snowfall
(Please See Item C.5))
F.6
Mean Number of Days with Snow Depth
(Please See Item C.6))
F.7
Mean Number of Clear Days (Sunrise to Sunset):
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Summary of the Day First Order (TD-3210) database (NOAA, 2000b). The original data is in tenths of sky cover according to the following: clear (0.0 - 0.1); scattered (0.1 - 0.5); broken (0.6 to 0.9); and overcast (1.0). This element is given as the number of whole days.
The monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the number of days with mean sky cover less than or equal to 0.3 for a given month. The daily values were computed from the mean of observations for the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean number of clear days.
F.8
Mean Number of Partly Cloudy Days (Sunrise to Sunset):
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Summary of the Day First Order (TD-3210) database (NOAA, 2000b). The original data is in tenths of sky cover according to the following: clear (0.0 - 0.1); scattered (0.1 - 0.5); broken (0.6 to 0.9); and overcast (1.0). This element is given as the number of whole days.
The monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the number of days with mean sky cover greater than 0.3 and less than or equal to 0.7 for a given month. The daily values were computed from the mean of observations for the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean number of partly cloudy days.
F.9
Mean Number of Cloudy Days (Sunrise to Sunset):
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Summary of the Day First Order (TD-3210) database (NOAA, 2000b). The original data is in tenths of sky cover according to the following: clear (0.0 - 0.1); scattered (0.1 - 0.5); broken (0.6 to 0.9); and overcast (1.0). This element is given as the number of whole days.
The monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the number of days with mean sky cover greater than 0.7 for a given month. The daily values were computed from the mean of observations for the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean number of cloudy days.
F.10
Mean Number of Days with Heavy Fog:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Summary of the Day First Order (TD-3210) database (NOAA, 2000b). The original data and this element are given as whole days.
The monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the number of days with at least one occurrence of heavy fog for a given month. The daily values included observations for the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean number of days with heavy fog. Heavy ice fog was considered as heavy fog through 1964. Heavy fog is defined as reducing visibility to 0.25 mile or less.
F.11
Mean Number of Days with Thunder:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Summary of the Day First Order (TD-3210) database (NOAA, 2000b). The original data and this element are given as whole days.
The monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the number of days with at least one occurrence of thunder for a given month. The daily values included observations for the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean number of days with thunder. 
G. Other Elements
G.1
Mean Total Heating Degree Days
(Please See Item A.14))
G.2
Record Maximum Heating Degree Days
(Please See Item A.15))
G.3
Mean Total Cooling Degree Days
(Please See Item A.16))
G.4
Record Maximum Cooling Degree Days
(Please See Item A.17))
G.5
Mean Percentage of Visibility <= 0.25 Mile:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Surface Airways Hourly (TD-3280) database (NOAA, 2000a). The original data is given as a code corresponding to a given horizontal distance of visibility. This element is given as a percentage.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the percentage of hours with visibility less than or equal to 0.25 mile for a given month. The annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the percentage of hours with visibility less than or equal to 0.25 mile for each calendar year. Monthly and annual mean extreme wind speeds for the identified percentile were computed by determining the percentile from all hourly averaged wind speed observations for the month and year.
G.6
Mean Percentage of Visibility <=1 Mile:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Surface Airways Hourly (TD-3280) database (NOAA, 2000a). The original data is given as a code corresponding to a given horizontal distance of visibility. This element is given as a percentage.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the percentage of hours with visibility less than or equal to 1 mile for a given month. The annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the percentage of hours with visibility less than or equal to 1 mile for each calendar year. Monthly and annual mean extreme wind speeds for the identified percentile were computed by determining the percentile from all hourly averaged wind speed observations for the month and year.
G.7
Mean Percentage of Visibility <=3 Miles:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Surface Airways Hourly (TD-3280) database (NOAA, 2000a). The original data is given as a code corresponding to a given horizontal distance of visibility. This element is given as a percentage.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the percentage of hours with visibility less than or equal to 3 miles for a given month. The annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the percentage of hours with visibility less than or equal to 3 miles for each calendar year. Monthly and annual mean extreme wind speeds for the identified percentile were computed by determining the percentile from all hourly averaged wind speed observations for the month and year.
G.8
Mean Percentage of Visibility <=10 Miles:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Surface Airways Hourly (TD-3280) database (NOAA, 2000a). The original data is given as a code corresponding to a given horizontal distance of visibility. This element is given as a percentage.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the percentage of hours with visibility less than or equal to 10 miles for a given month. The annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the percentage of hours with visibility less than or equal to 10 miles for each calendar year. Monthly and annual mean extreme wind speeds for the identified percentile were computed by determining the percentile from all hourly averaged wind speed observations for the month and year.
G.9
Mean Percentage of Visibility> 10 Miles:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Surface Airways Hourly (TD-3280) database (NOAA, 2000a). The original data is given as a code corresponding to a given horizontal distance of visibility. This element is given as a percentage.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the percentage of hours with visibility greater than 10 miles for a given month. The annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the percentage of hours with visibility greater than 10 miles for each calendar year. Monthly and annual mean extreme wind speeds for the identified percentile were computed by determining the percentile from all hourly averaged wind speed observations for the month and year.
G.10
Mean Sunshine Percentage:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's U.S. Stations 1961-1990 Monthly Normals for the Atypical Climate Elements (TD-9641) database (NOAA, 1997b). The original data and this element are given as a percentage of possible sunshine.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the monthly means. The monthly means were computed from the daily values. The daily values were computed as the number of hours of sunshine observed out of the hours of sunshine possible for the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean values.
G.11
Mean Sunshine Total Hours:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's U.S. Stations 1961-1990 Monthly Normals for the Atypical Climate Elements (TD-9641) database (NOAA, 1997b). The original data and this element are given as the number of hours of observed sunshine.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the total hours of sunshine for a given month. The monthly total hours were computed from the daily values. The daily values were computed as the total number of hours of sunshine observed for the 24-hour period ending at the time of observation for a given station. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean values.
G.12
Mean Sky Cover (Sunrise to Sunset):
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Summary of the Day First Order (TD-3210) database (NOAA, 2000b). The original data is in tenths of sky cover according to the following: clear (0.0 - 0.1); scattered (0.1 - 0.5); broken (0.6 to 0.9); and overcast (1.0). This element is given as a percentage.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the monthly means. The monthly means were computed from the daily values. The daily values were computed as the mean of the hourly daylight sky cover observations where tenths of sky cover were converted to percentages (i.e., 0.1=10%, etc.) The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean values.
G.13
Mean Number of Clear Days (Sunrise to Sunset)
(Please See Item F.7))
G.14
Mean Number of Partly Cloudy Days (Sunrise to Sunset)
(Please See Item F.8))
G.15
Mean Number of Cloudy Days (Sunrise to Sunset)
(Please See Item F.9))
G.16
Mean Relative Humidity:
This element was computed using data from the National Climatic Data Center's Surface Airways Hourly (TD-3280) database (NOAA, 2000a). The original data and this element are measured as a percentage.
The mean monthly values were computed by taking the 30-year mean of the monthly means. The monthly means were computed from the daily values. The daily values were computed as the mean of relative humidity values for the 24 hourly observations. The mean annual value was computed by taking the 30-year mean of the yearly means. The yearly means were computed by averaging their 12 monthly mean values.
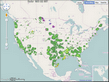
G.17
Hail Events with Diameters>=0.75 Inch
The hail data set was provided by the U.S. Air Force Combat Climatology Center, Air Weather Service. Data originated from the Storm Prediction Center, NOAA. The information is based on hail reports published in NCDC's Storm Data. The selected period of record is 1961-1990. Hail data are based on point reports of individual hail events.
Hail event maps report individual hail events that are either severe (hail size exceeding 0.75" in diameter) or large (hail size exceeding 1" in diameter). Hail day maps report the mean annual number of days of hail. These maps are based on gridded hail event data in a Geographic Information System. The frequency of occurrence of reported hail events was somewhat dependent on population density and technology (for example, NEXRAD), therefore take care when interpreting this data.
G.18
Tornado Tracks:
The tornado track data set was provided by the U.S. Air Force Combat Climatology Center, Air Weather Service. Data originated from the Storm Prediction Center, NOAA. The information is based on tornado reports published in NCDC's Storm Data. The selected period of record is 1961-1990.
The tornado data were quality controlled for spatial consistency and checked for valid reportable values. Tornado tracks are presented by decade, season, and Fujita scale. The frequency of occurrence of reported tornado tracks was somewhat dependent on population density and technology (for example, NEXRAD). Therefore take care when interpreting this data.
The Fujita Scale (F-SCALE) corresponds to the following wind and damage descriptions:
Fujita Scale 0 (F0): Winds of 40-72 mph, MINIMAL DAMAGE (Some damage to chimneys, TV antennas, roof shingles, trees, and windows).
Fujita Scale 1 (F1): Winds of 73-112 mph, MODERATE DAMAGE (Automobiles overturned, carports destroyed, trees uprooted).
Fujita Scale 2 (F2): Winds of 113-157 mph, MAJOR DAMAGE (Roofs blown off homes, sheds and outbuildings demolished, mobile homes overturned).
Fujita Scale 3 (F3): Winds of 158-206 mph, SEVERE DAMAGE (Exterior walls and roofs blown off homes. Metal buildings collapsed or are severely damaged. Forests and farmland flattened).
Fujita Scale 4 (F4): Winds of 207-260 mph, DEVASTATING DAMAGE (Few walls, if any, standing in well-built homes. Large steel and concrete missiles thrown far distances).
Fujita Scale 5 (F5): Winds of 261-318 mph, INCREDIBLE DAMAGE (Homes leveled with all debris removed. Schools, motels, and other larger structures have considerable damage with exterior walls and roofs gone. Top stories demolished).
G.19 - G.22
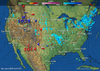
Seasonal Vegetation Cover:
These four seasonal images were derived from the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) satellite instrument and provided by NOAA/NESDIS/ORA and USGS/EROS Data Center. The images are in a PDF formatted file that can be read using Adobe Acrobat Reader.
The data represent maximum seasonal values of the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), with a range from 0.0 for bare soil to 1.0 for a fully vegetated surface. The seasonal values are for the climatological months (Dec/Jan/Feb for Winter, Mar/apr/May for Spring, Jun/Jul/aug for Summer, and Sep/Oct/Nov for Autumn, and are based on satellite data from 1993, 1995, 1996, 1997, and 1998.
NDVI is the most commonly used vegetation index. This index is computed by taking the difference between the near-IR and visible reflectance values divided by their sum. The NDVI, like most other vegetation indices, is premised on the greater reflectance by vegetation in the near-infrared wavelengths compared to visible wavelengths.
G.23 - G.25
Landfalling Hurricanes:
The hurricane landfall maps were created from latitude/longitude values for landfalling hurricanes as determined by the National Hurricane Center.
G.26
City Lights:
The city lights image is derived from Operational Linescan System (OLS) data collected by the U.S. Air Force Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP). The data were made available through NOAA/NESDIS/NGDC.
|